
As can be seen from the example, the company’s degree of operating leverage is 1.0x for both years. The company’s overall cost structure is such that the fixed cost is $100,000, while the variable cost is $25 per piece. If a company has low operating leverage (i.e., greater variable costs), each additional dollar of revenue can potentially generate less profit as costs increase in proportion to the increased revenue. Companies with a high degree of operating leverage (DOL) have a greater proportion of fixed costs that remain relatively unchanged under different production volumes. Here’s how you can use an Operating Leverage Calculator to understand how your company’s fixed and variable costs impact profitability.
Example Calculation of DOL
A higher degree of operating leverage means that a business has a high proportion of the fixed cost. A high DOL indicates that a company has a higher proportion of fixed costs, leading to greater sensitivity in operating income to changes in sales. Consider a company with fixed costs of $500,000, variable costs of $2 per unit, and selling price of $10 per unit. The degree of operating leverage (DOL) measures a company’s sensitivity to sales changes.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
One concept positively linked to operating leverage is capacity utilization, which is how much the company uses its resources to generate revenues. Increasing utilization infers increased production and sales; thus, variable costs should rise. If fixed costs remain the same, a firm will have high operating leverage while operating at a higher capacity.
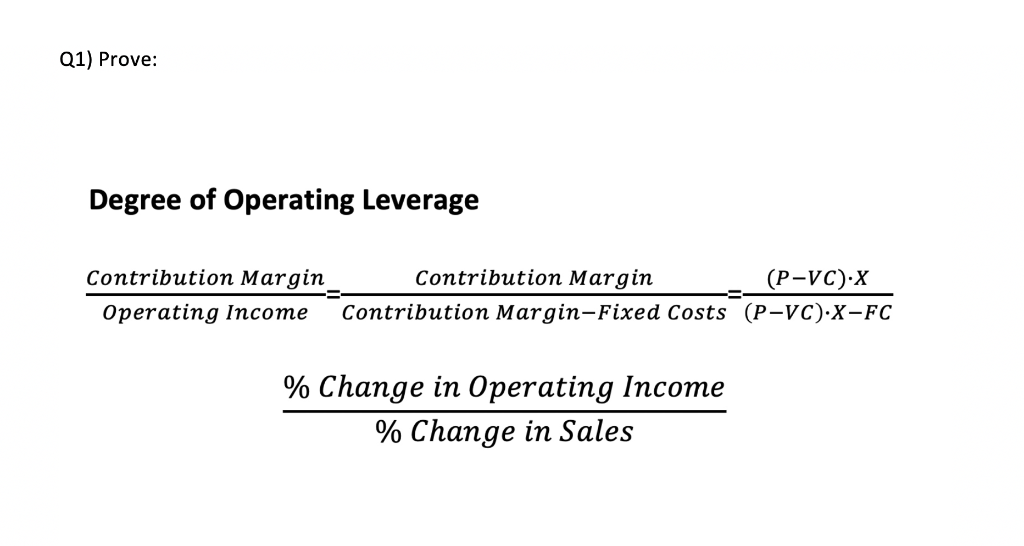
How to Calculate DOL?
The formula can reveal how well a company uses its fixed-cost items, such as its warehouse, machinery, and equipment, to generate profits. This tool helps you calculate the degree of operating leverage to understand how your company’s earnings might change with varying sales levels. The calculator washington d c tax preparation will provide the DOL value, which indicates the sensitivity of a company’s operating income to changes in sales volume. Under all three cases, the contribution margin remains constant at 90% because the variable costs increase (and decrease) based on the change in the units sold.
The Excel degree of operating leverage calculator is available for download below. The calculator is used to calculate the DOL by entering details relating to the quantity of units sold, the unit selling price and cost price, and the fixed costs of the business. By calculating the DOL, you can understand how fixed costs influence your business profitability.
Degree of Operating Leverage Formula
- In practice, the formula most often used to calculate operating leverage tends to be dividing the change in operating income by the change in revenue.
- The only difference now is that the number of units sold is 5mm higher in the upside case and 5mm lower in the downside case.
- Even if sales increase, fixed costs do not change, hence causing a larger change in operating income.
- In other words, any increase in sales might cause an increase in operating income.
- By calculating the DOL, you can understand how fixed costs influence your business profitability.
- Assess different scenarios by adjusting sales volumes and costs to see how your operating income would be impacted.
That indicates to us that this company might have huge variable costs relative to its sales. Similarly, we can conclude the same by realizing how little the operating leverage ratio is, at only 0.02. The management of XYZ Ltd. wants to calculate the current degree of operating leverage of its company. Here, the variable cost per unit is Rs.12, while the total fixed cost is Rs.1,00,000. This ratio summarizes the effects of combining financial and operating leverage, and what effect this combination, or variations of this combination, has on the corporation’s earnings. Not all corporations use both operating and financial leverage, but this formula can be used if they do.
Degree of operating leverage can never be negative because it is a ratio of two positive numbers (sales and operating income). As such, the DOL ratio can be a useful tool in forecasting a company’s financial performance. Degree of operating leverage closely relates to the concept of financial leverage, which is a key driver of shareholder value. DOL can help any company to determine the suitable level of operating leverage.
Welcome to the fascinating world of the Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL)! If you’re eager to understand how changes in sales impact your operating income, you’re in the right place. This guide will walk you through the ins and outs of using the Degree of Operating Leverage Calculator, all while keeping things engaging and lighthearted.